Rising demand for stronger crypto security and direct control has pushed non-custodial wallets into the mainstream. According to Business Research Insights’s report, the global non-custodial wallet market was about $1.1B in 2024 and may reach $3.5B by 2033 (CAGR ~13.7%).
Given this growth and increasing demand, it’s essential to understand the nature and security requirements of a non-custodial wallet to avoid unnecessary risks & asset loss. This article provides a clear guide on non-custodial wallets: what they are, how they work, and how to use them safely.
What is a Non-custodial Wallet?
A non-custodial wallet is a crypto wallet where the user alone stores and manages the private keys. This gives full control over assets and requires self-approval of every transaction, unlike a custodial wallet, where a third party holds the keys and can move funds on the user’s behalf.
In simple terms, no one (not even the wallet developer) can freeze, access, or transact the assets within the wallet without the user's permission. This model is commonly referred to as self-custody.

Custodial vs. Non-custodial Wallet: What is the difference?
In stark contrast with a non-custodial wallet, a custodial wallet delegates the management of the user's private keys to a third party, most commonly the service provider itself, such as a cryptocurrency exchange. With a custodial wallet, this third party holds the ultimate authority to control, access, and transact the user's assets.
Key differences between custodial wallet vs. non-custodial wallet include:
| Criterion | Custodial Wallet (third party holds keys) |
Non-custodial Wallet (you hold keys) |
|---|---|---|
| Private key ownership | Custodian holds or co-controls private keys. | User fully owns the private key/seed phrase. |
| Asset control | Third party can freeze/restrict per terms or regulation. | Full user control; transactions occur only when you sign. |
| Recovery model | Account recovery via KYC/password reset and support. | Recovery via seed phrase or social/MPC recovery; lost seed can mean lost access. |
| Trust assumptions | Must trust custodian (insolvency, breaches, misuse risks). | Minimal intermediary trust; main risks are user/device security. |
| Security & attack surface | Centralized infrastructure—professionally managed but an attractive target. | Decentralized—avoids exchange hacks but prone to phishing/bad signing/malware. |
| Regulation & KYC/AML | Typically requires KYC and complies with geo-restrictions. | Often no KYC; higher privacy (varies by chain/dApp). |
| DeFi/dApp access | Limited to the exchange’s ecosystem or curated integrations. | Direct connection to any dApp; you manage approvals and limits. |
| Ongoing costs | Possible custody/withdrawal fees and internal limits. | No custody fees; pay network gas and possibly hardware costs (for cold wallets). |
How Non-custodial Wallet works
A non-custodial wallet generates and stores keys locally on the user’s device. The wallet provides an interface to create transactions that are then broadcast to the blockchain.
When setting up a non-custodial wallet, the user is provided with important keys, including:
- Public Key: An alphanumeric string used to receive assets into the wallet. This key can be shared publicly and is typically shortened into the wallet address.
- Private Key: An alphanumeric string required to access the wallet and authorize outbound transactions (sending assets). This key must be kept strictly confidential.
- Seed Phrase (Mnemonic Seed): A sequence of 12 to 24 random English words used to restore or access multiple wallets simultaneously. Like the private key, it must be kept secret.
The private key and seed phrase are encrypted and stored in a secure, isolated area on the user’s device, accessible only by the user. This information is paramount as it directly controls the associated assets. Therefore, users are required to safely record and back up their private key and seed phrase to ensure wallet recovery in the event of device loss, damage, or malfunction.
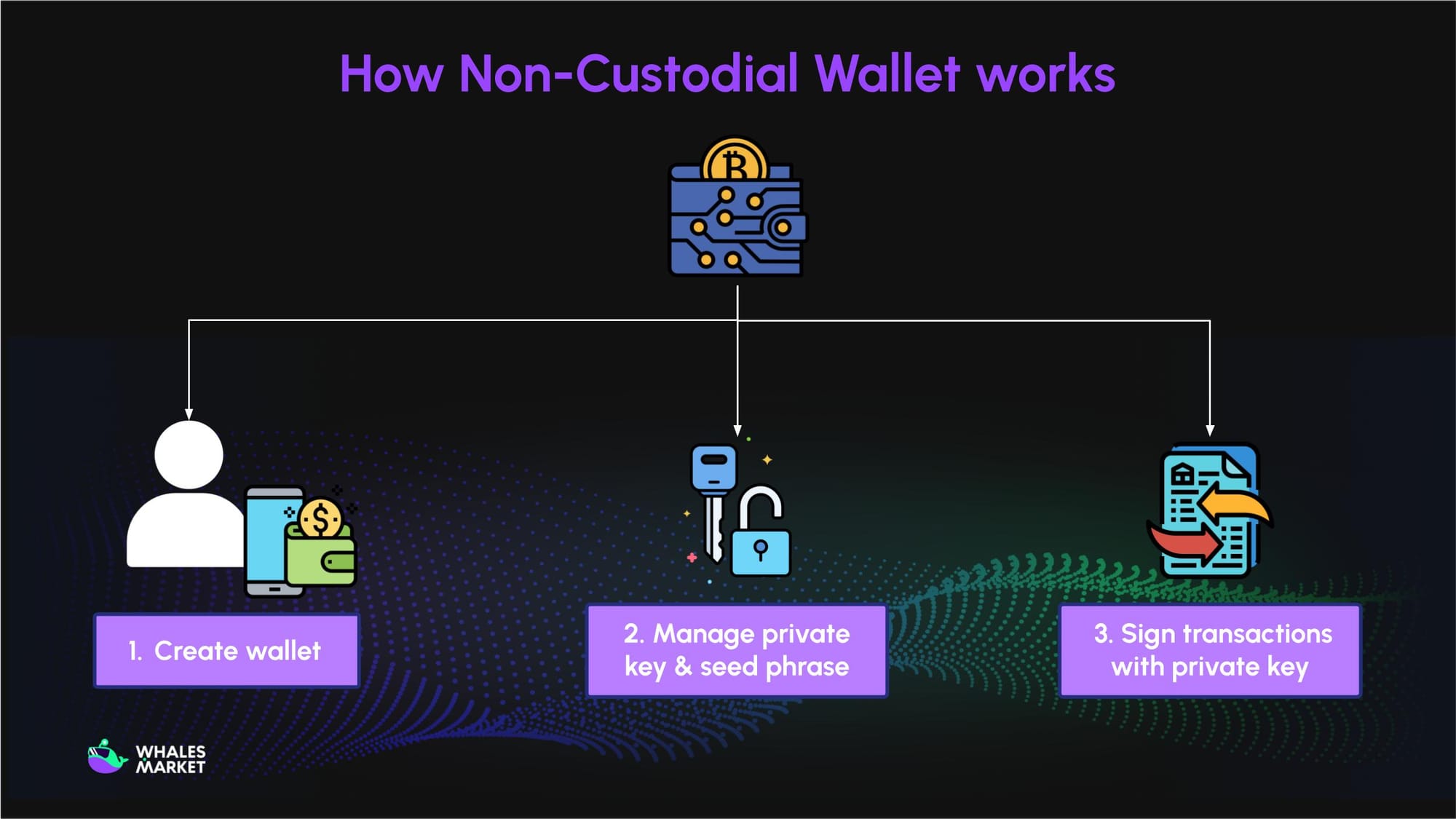
When a user executes a transaction, they must digitally sign it within the non-custodial wallet using their private key to cryptographically prove ownership and authorize the transfer of assets on the blockchain. This process is essential for broadcasting the verified transaction to the network.
In short, non-custodial wallets keep keys with the user, use those keys to sign and broadcast on-chain transactions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Non-custodial Wallet
Advantages (Pros)
- Users’ control over assets: Users have absolute control over their private keys, recovery phrase, and consequently, their funds. This adheres to the principle of "not your keys, not your coins."
- Censorship-resistant: Assets are not held on a third party platform, making them immune to the risks of platform hacks, sudden insolvency, or operational failure of a custodian.
- High privacy: Non-custodial wallets typically do not require KYC/AML verification, allowing users to interact with the blockchain ecosystem with a higher degree of anonymity.
- No limitations & Full access to dApps: Transactions on custodial wallets may be restricted in terms of withdrawal limits or even freezing of your account by a third-party. In this context, non-custodial wallets are unrestricted as the freedom as well as responsibility of the assets is completely in your hands. Users can directly connect and interact with the entire decentralized finance (DeFi) and web3 ecosystem.
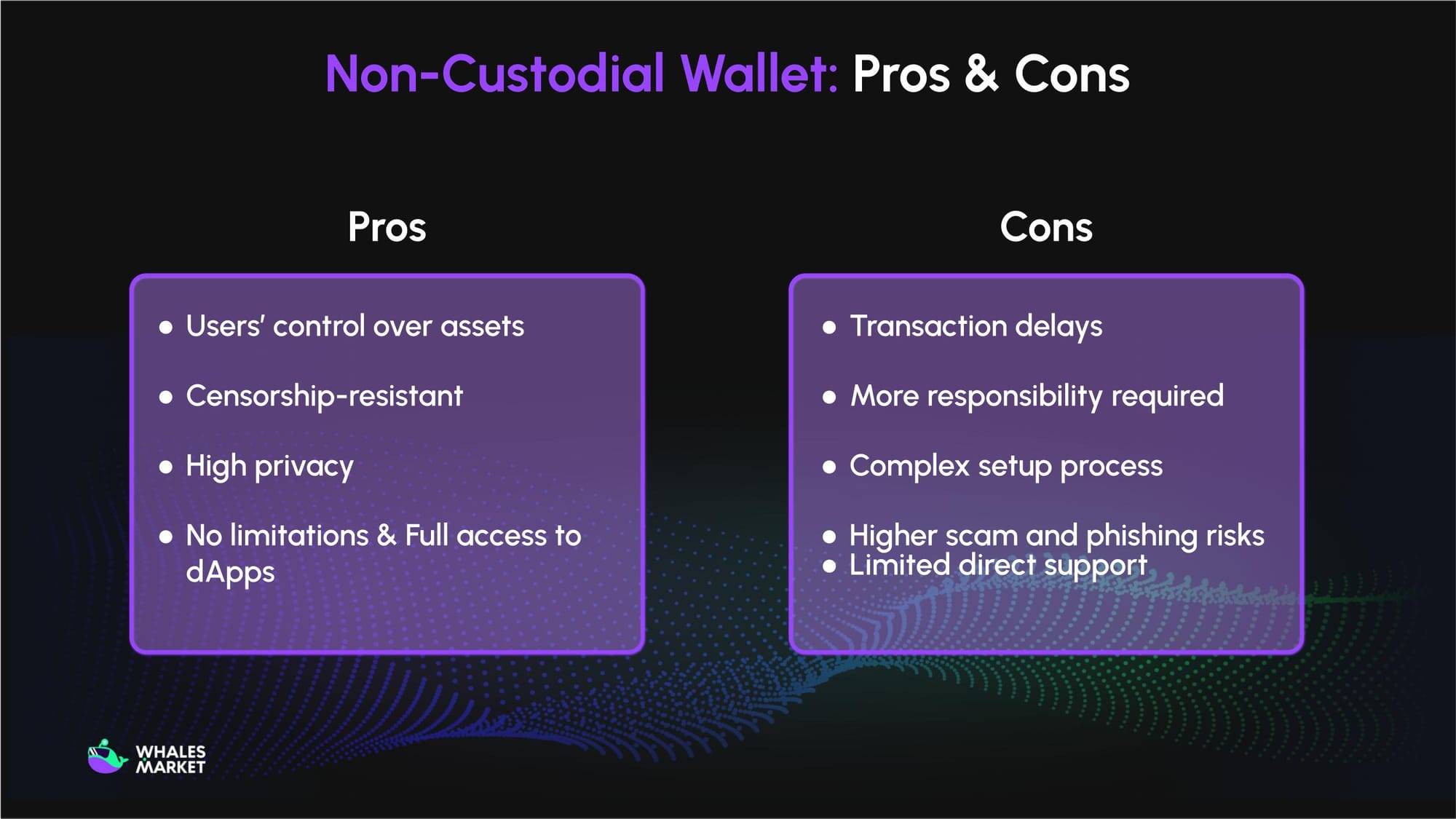
Disadvantages (Cons)
- Transaction delays: All movements on non-custodial wallet settle directly on-chain, so confirmation time depends on network congestion and fee settings. If gas is set too low or the chain is congested, transactions can sit pending or fail. Unlike custodial internal transfers, there’s no instant off-chain fast path.
- More responsibility required: With self-custody, private keys and seed phrases are the only way to control funds. If they’re lost, stolen, or exposed, assets can be irretrievable, there’s no password reset or bank-style reversal. This absolute control is powerful, but unforgiving.
- Complex setup process: Non-custodial wallets require understanding addresses, networks, gas, and approvals. Missteps (like sending to the wrong chain or signing risky permissions) can be costly. Users must learn basic operational security (backups, device hygiene) to stay safe.
- Higher scam and phishing risks: Because there is no third-party guarantor, non-custodial wallets are a prime target for attackers. They go after seed phrases and signing prompts via fake sites, wallet pop-ups, and impostor support. Since transactions are self-signed, a single mistaken approval can grant malicious access and lead to the loss of all assets.
- Limited direct support: There’s no centralized help desk to undo a wrong transfer, recover a lost key, or freeze funds. Most assistance comes from documentation and community forums. This independence is part of self-custody, but it also means problems demand self-recovery plans.
How to stay safe when using Non-custodial Wallet
Since a non-custodial wallet places sole responsibility for security on the user, adhering to best practices is essential to prevent permanent loss of assets.
- Back up the seed phrase offline: Write the 12–24 words on paper or steel and store them in two safe locations. Never screenshot or upload it, anyone who sees the seed can control the wallet.
- Use a hardware wallet for larger balances: Keep day-to-day funds in a hot wallet and savings on a hardware device. Hardware signing keeps private keys off the internet and reduces remote-hack risk.
- Verify links and downloads: Only use bookmarked, official sites and app store pages linked from the project’s website. Fake sites and browser extensions are a common way seeds and signatures get stolen.
- Read every signing prompt: Check what you’re approving, especially unlimited spend allowances. If the permissions look unusual or unclear, cancel first and investigate.
- Start small on new dApps and bridges: Send a tiny test transaction to confirm the route, fees, and destination address. Scale up only after the trial behaves exactly as expected.
- Review and revoke token allowances: Over time, approvals accumulate and can be abused if a dApp is compromised. Use your wallet’s permissions panel (or a trusted revoker) to remove unused approvals.
- Keep software and firmware updated: Update wallet apps, browser, and hardware-wallet firmware to patch vulnerabilities. Out-of-date software is a frequent entry point for exploits.
- Be scam-aware, no one needs your seed: Legitimate teams will never ask for seed phrases or private keys. Ignore unsolicited support messages and random claim links, even if they look official.
Conclusion
Non-custodial wallets are rising because they deliver what crypto promises: control, security, and true self-custody. When the private keys stay with the owner, third-party risk falls and asset independence increases, ideal for a DeFi landscape that rewards sovereignty.
The trade-off is responsibility. Users should back up seed phrases, follow sound security practices, and understand basic on-chain actions. With those habits in place, a non-custodial wallet becomes a dependable, future-proof way to manage and grow digital assets.
FAQs
Is Coinbase wallet non custodial?
Yes. Coinbase Wallet (the standalone app) is non-custodial, keys are user-controlled. This is separate from a Coinbase exchange account, which is custodial.
What does Non-custodial Wallet mean?
A non-custodial wallet means a crypto wallet where the private keys are generated and controlled by the user, not a third party. This enables full control over funds and on-chain actions, along with full responsibility for security and recovery.
What's the difference between a custodial and a non-custodial wallet?
Custodial wallets hold users’ keys and can process transfers internally, often with simpler recovery but added counterparty risk.
Non-custodial wallets leave keys with the user, enabling censorship resistance and direct dApp access, but require careful key management and on-chain fee payment.
How do I choose a non-custodial crypto wallet?
To choose a non-custodial crypto wallet, consider these criteria:
- Evaluate security: Open-source code, audits, hardware-wallet support.
- Good UX: Clean signing prompts, network support
- Ecosystem fit: Which chains/dApps it supports.
- Recovery options: Seed phrase, passkeys, social recovery.
- Reputation/history of security incidents.
Which non-custodial wallet is the safest?
“Safest” depends on the threat model. For long-term storage, a hardware wallet (e.g., Ledger, Trezor) paired with a reputable software wallet is considered strongest. For daily use, pick audited, widely used wallets with rigorous permission controls and phishing protections.
Who should use a non-custodial wallet?
Users who want self-sovereign control, direct access to DeFi and NFTs, and minimal reliance on intermediaries. It suits those willing to manage seed phrases and accept that lost keys usually mean irretrievable funds.

