Instead, Ethereum’s founders set out to build a new kind of global, decentralized computing platform that takes the security and openness of blockchains and extends those attributes to a vast range of applications.
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum is a decentralized and open-source Layer 1 blockchain that enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications, also known as dApps. The blockchain was developed by Vitalik Buterin and launched in 2015.
Ethereum extends the blockchain’s capabilities beyond digital currency, enabling programmable agreements and applications across various industries. Unlike Bitcoin, which primarily functions as a digital currency and store of value, Ethereum aims to create an open, on-chain financial world, thereby starting the era of DeFi.

Ethereum, Ether vs. ETH: What’s the difference?
It's a common point of confusion, but the distinction is simple.
- Ethereum is the name of the entire decentralized blockchain network, think of it as a global operating system.
- Ether is the native cryptocurrency, or "fuel," that powers all transactions on that network.
- ETH is simply the ticker symbol for Ether, just like USD is for the US Dollar.
The History of Ethereum: From Concept to Global Supercomputer
The Vision (2013 - 2015): A Programmable Blockchain
In 2013, a young developer named Vitalik Buterin imagined a blockchain that could do more than record transactions, one that could run any program through smart contracts. Backed by co-founders like Gavin Wood and Joseph Lubin, this idea took shape as Ethereum, a decentralized “world computer.”
A year later, its 2014 ICO raised over $18M, proving the concept had global appeal. When the mainnet launched in July 2015, Ethereum didn’t just introduce a new coin, it introduced a new computing paradigm: decentralized applications (dApps).
The DAO Hack (2016): A Test of Principles
Success brought challenges. In 2016, “The DAO,” a decentralized investment fund, was hacked through a reentrancy attack due to a smart-contract flaw. This resulted in a loss of over $60M worth of Ether.
*Reentrancy attack occurs when an attacker exploits the reentrancy vulnerability in a smart contract to steal funds or manipulate the contract’s state in unintended ways.
The crisis divided the community. Most developers chose a hard fork to reverse the hack, giving birth to today’s Ethereum (ETH). A minority who rejected the rollback continued the original chain, now known as Ethereum Classic (ETC). This event cemented Ethereum’s identity as a community guided by both ethics and innovation.

The Boom Years (2017 - 2021): ICOs, DeFi, and NFTs
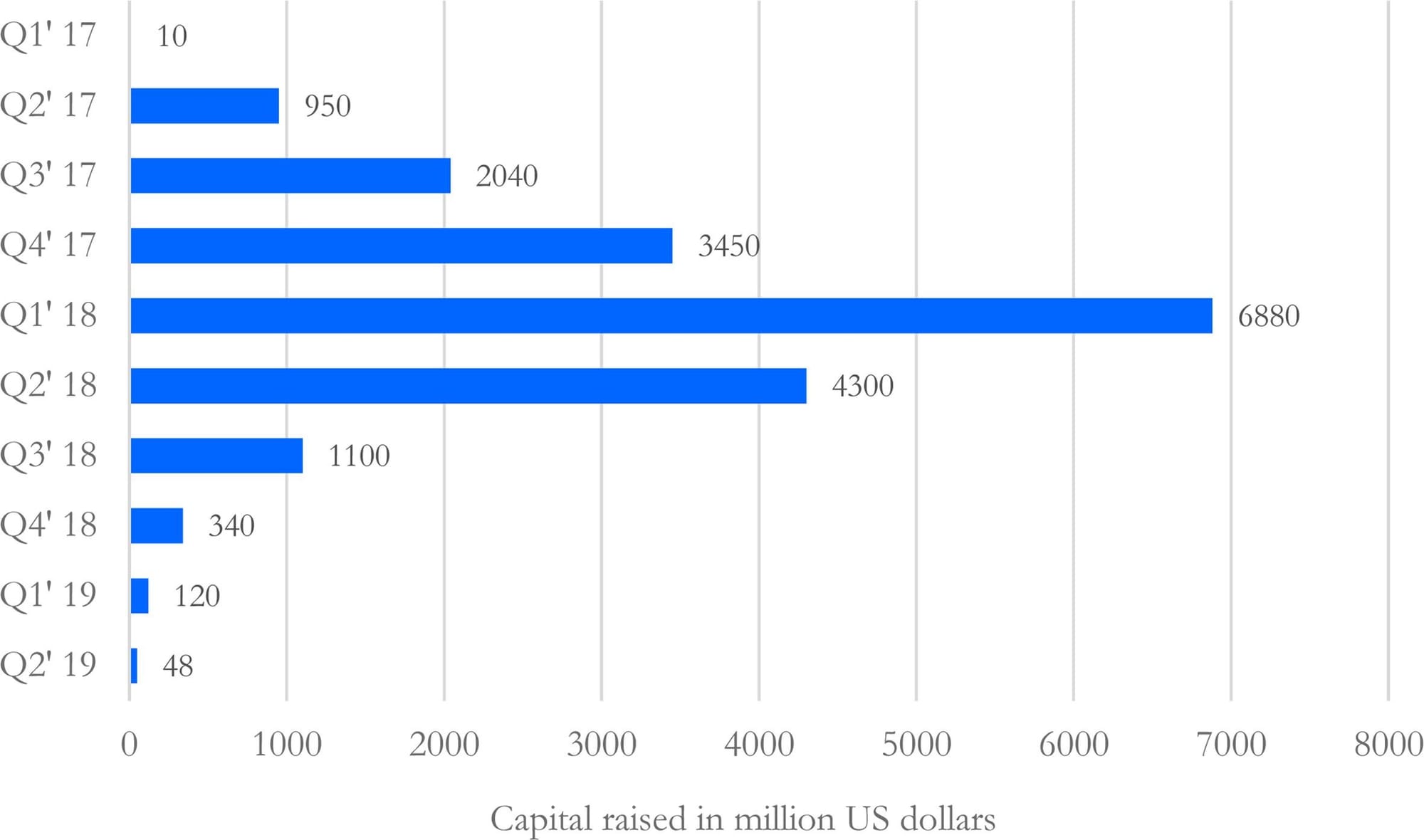
Ethereum soon became the heartbeat of blockchain innovation. The 2017 ICO boom, powered by the ERC-20 token standard, turned it into the world’s fundraising engine.
Between early 2017 and October 2018, ICOs pulled in about $20 billion worldwide: $7 billion in 2017 and $12 billion in 2018. In addition, Ethereum hosts over 90 % of ICOs in 2018, raising a total of over $12 B.
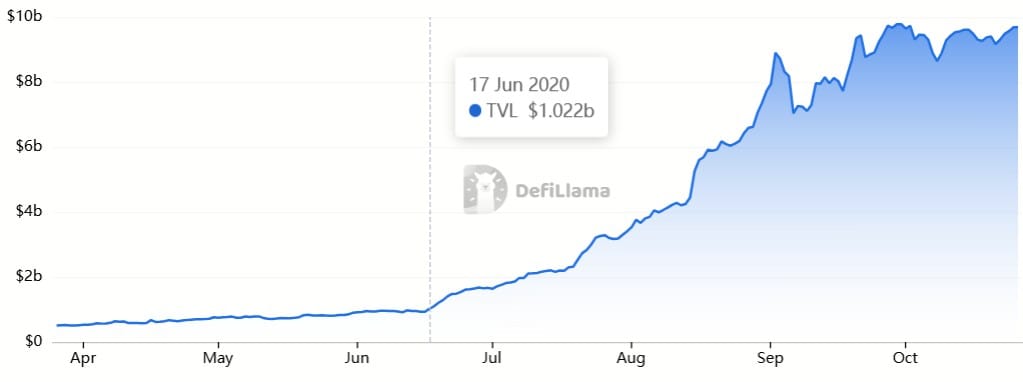
When that wave subsided, DeFi Summer 2020 reignited activity, protocols like Uniswap, Compound, and Aave pushed Total Value Locked (TVL) increase by about $1B every week, and sometimes far sooner.
Ethereum’s next breakout came through art and memes. In 2021, NFTs captured the cultural zeitgeist as projects like CryptoPunks and Bored Ape Yacht Club turned pixelated avatars into mainstream status symbols. In March 2021, digital artist Beeple sold an NFT artwork for $69M at Christie’s.
But success came at a cost: Ethereum’s popularity caused high gas fees and network congestion, exposing the urgent need to scale.
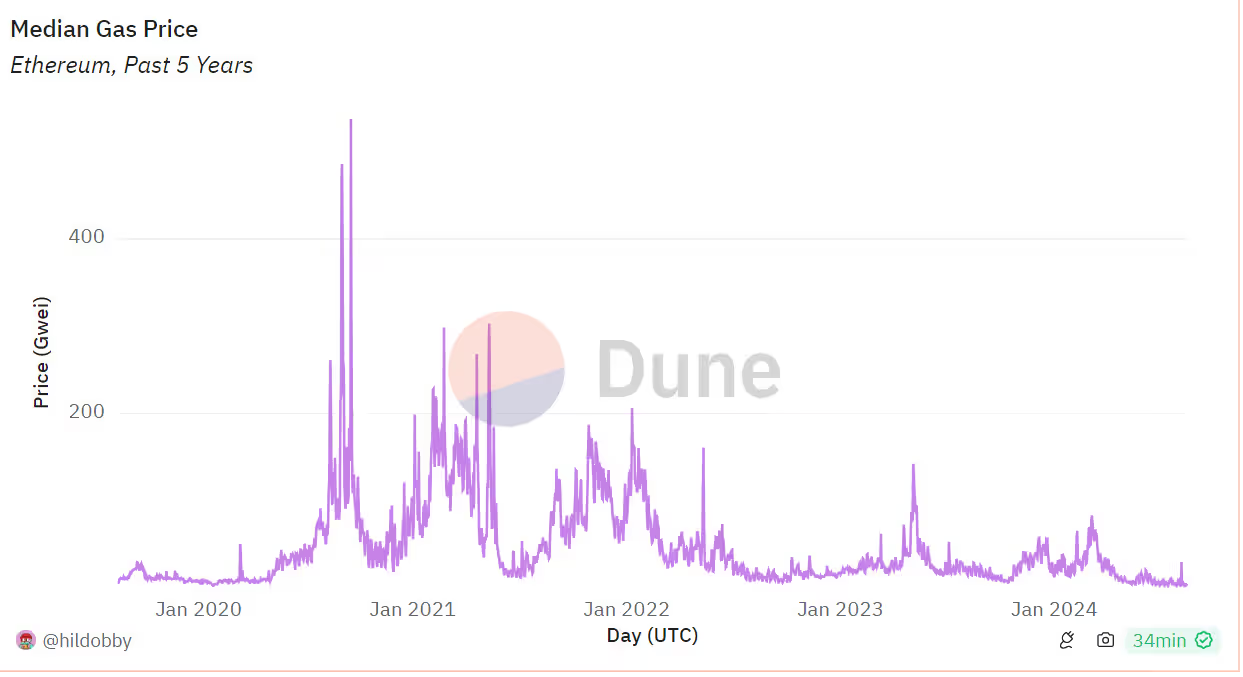
The Great Transition (2020 - 2024): Reinventing the Core
Ethereum’s developers responded with one of the most ambitious upgrades in tech history, a shift from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake and a complete redesign of how the network scales, aiming to reduce gas fees and improve transaction speeds.
- The Beacon Chain (2020): Introduced staking and a new PoS consensus layer running alongside the old chain.
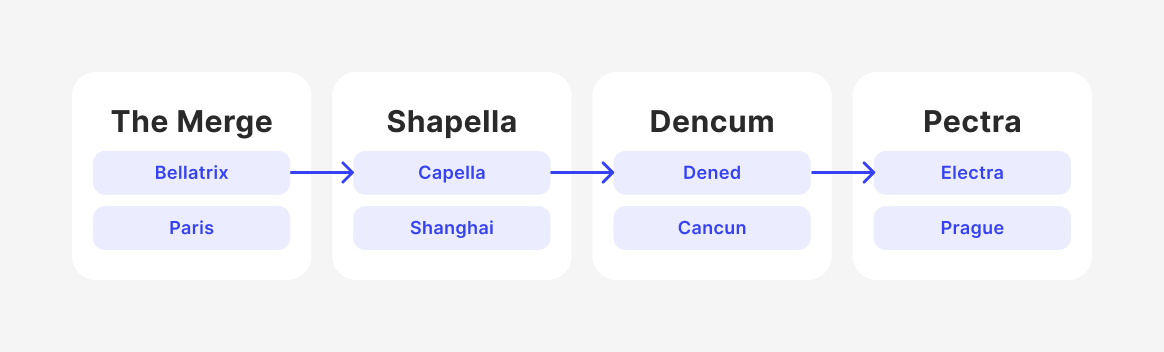
- The Merge (2022): Ethereum’s defining moment, merging both chains into one unified PoS network, cutting energy use by 99.9%.
- The Shanghai Upgrade (2023): Enabled staked ETH withdrawals, making staking accessible and liquid.
- The Dencun Upgrade (2024): Rolled out Proto-Danksharding (EIP-4844), slashing Layer-2 fees and empowering rollups like Optimism and Arbitrum to scale Ethereum to millions of users.
- The Pectra Upgrade (2025): The next major milestone combining Prague (execution layer) and Electra (consensus layer) upgrades. It aims to improve validator usability, introduce account abstraction (EIP-3074), and optimize transaction efficiency, laying further groundwork for full sharding and mass adoption.
Financial Mainstreaming (2024 - Now): The Spot Ethereum ETF
In 2024, Ethereum reached a new milestone beyond technology: mainstream financial validation. Following Bitcoin’s lead, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) approved the first spot Ethereum ETFs in May 2024, with trading commencing that July.
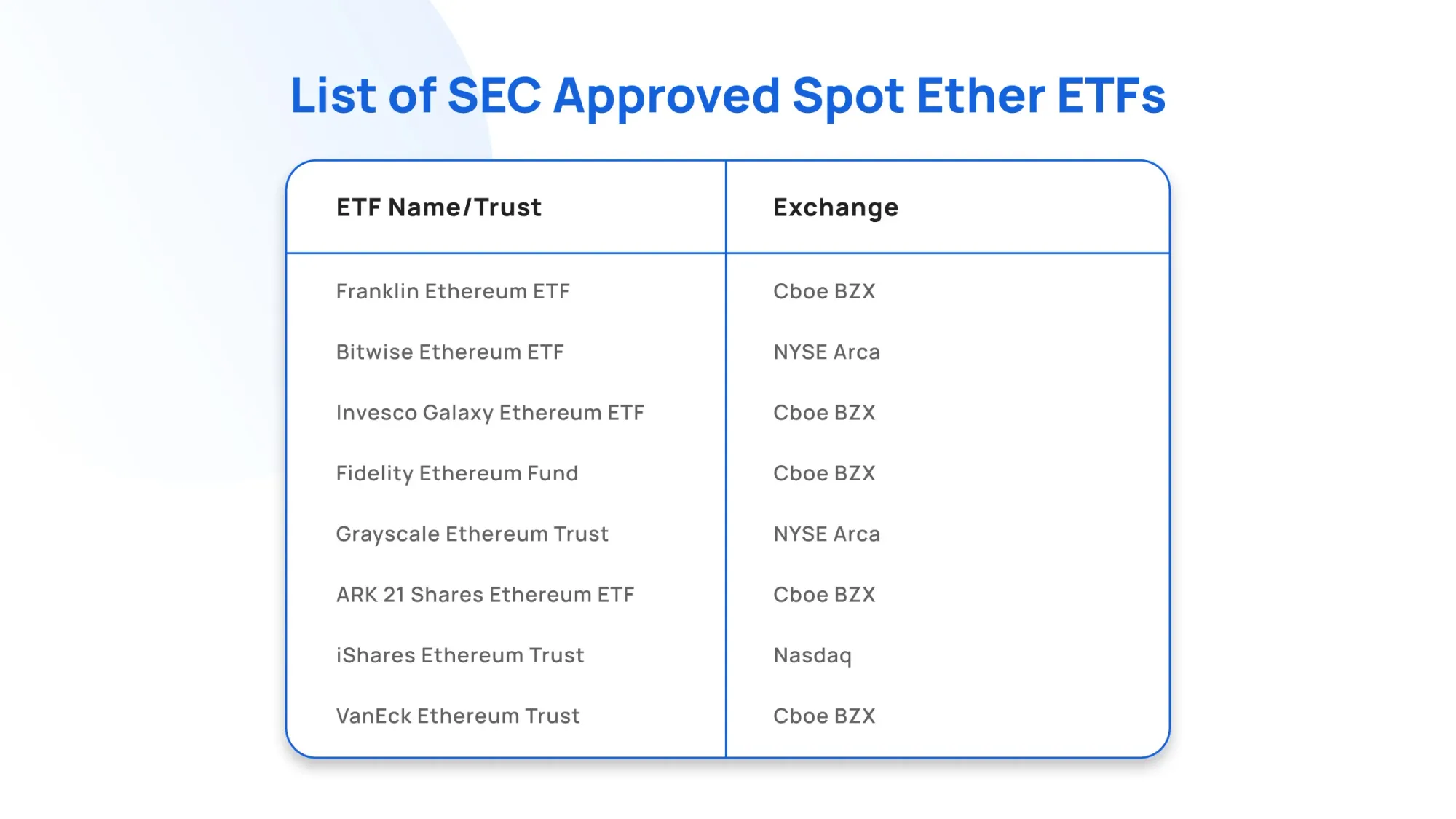
This approval marked a turning point for the asset class, offering investors regulated exposure to ETH through traditional brokerage platforms. The move underscored Ethereum’s growing legitimacy as a commodity, while accelerating institutional participation and integration between traditional finance (TradFi) and the Web3 ecosystem.
How Ethereum Works
Ethereum functions as a decentralized global computer, or "world computer." It’s a single, shared network of thousands of computers (nodes) that can execute applications, store data, and process transactions without a central owner.
Its operation relies on Five key components: the consensus mechanism, staking, nodes, the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), and smart contracts.
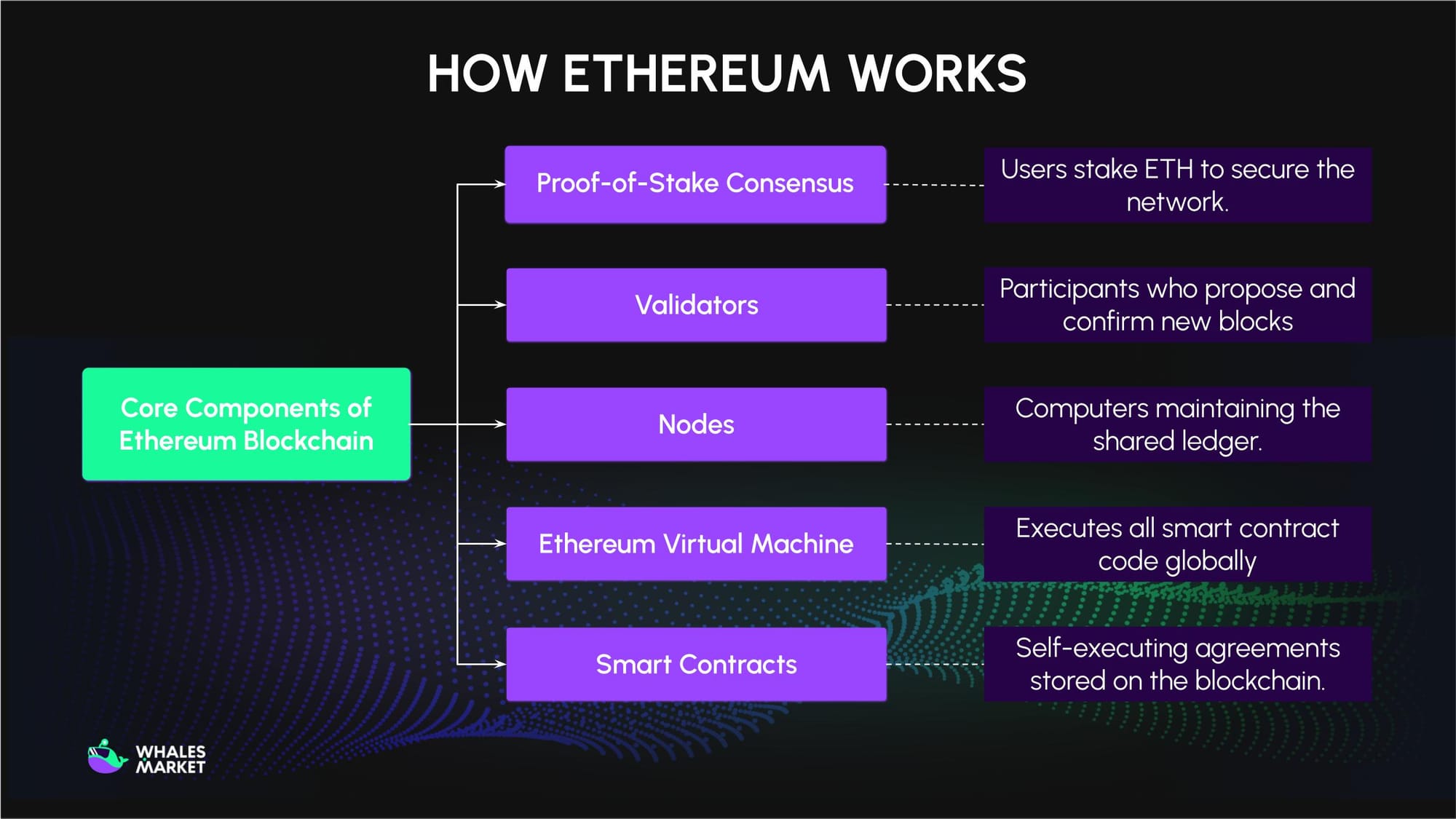
- Consensus mechanism: Ethereum’s blockchain was initially secured by the Proof-of-Work (PoW) mechanism, similar to Bitcoin. After the Merge upgrade in 2022, it transitioned to Proof-of-Stake (PoS), where users can stake ETH to become validators. These validators confirm transactions and maintain the network’s security, earning rewards in ETH for their participation.
- Staking: Refers to participating in the Proof-of-Stake consensus process. To become a validator, a user must deposit 32 ETH into a smart contract. Validators are responsible for running nodes, verifying transactions, and proposing new blocks. Smaller holders can still contribute by joining staking pools, earning proportional rewards.
- Nodes: Individual computers or servers participating in the Ethereum network by maintaining a copy of the blockchain and following the network's rules.
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): A piece of software that each node has to run. The EVM ensures that all nodes produce identical results from the same code, creating a system that is consistent, secure, and trustless.
- Smart contracts: Self-executing programs stored on the blockchain. They function as automated “if-then” agreements: when specific conditions are met, the contract executes its programmed actions automatically. Once deployed, smart contracts cannot be altered and always perform as written. They serve as the foundation of Ethereum’s ecosystem, powering decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, dApps, and NFTs.
Ethereum Token Standard
Ethereum’s flexibility comes from its ability to host and manage tokens that represent a wide range of assets, from cryptocurrencies and stablecoins to NFTs and governance tokens. To ensure these assets interact seamlessly across wallets, exchanges, and dApps, Ethereum uses standardized rules known as token standards.
Here are the most important standards:
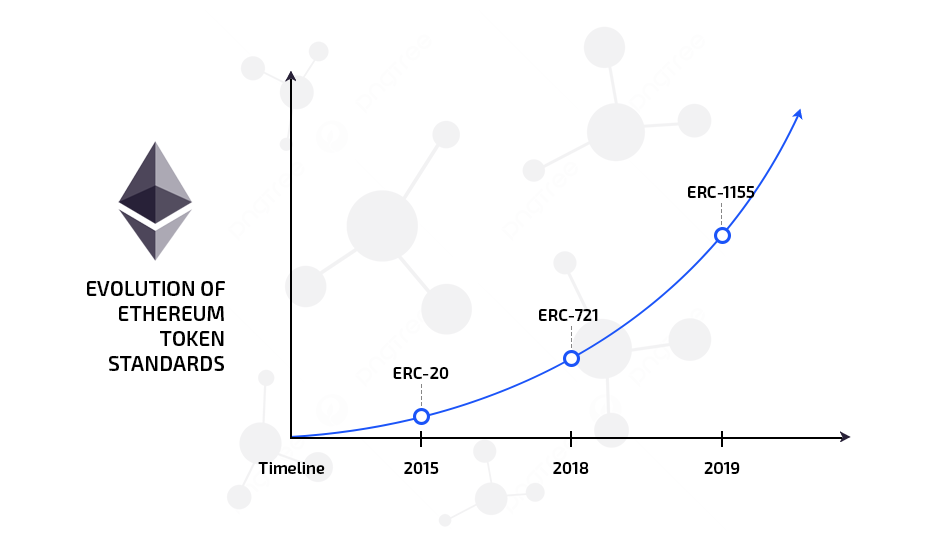
- ERC-20 - The Fungible Token Standard: Introduced in 2015, this standard defines how fungible tokens behave on Ethereum. Each token is interchangeable and has the same value as another of its kind. Most popular cryptocurrencies built on Ethereum follow this standard, including USDT, LINK, UNI…
- ERC-721 - Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Proposed in 2018, this standard introduced non-fungible tokens, where each token is unique and distinguishable from others. This standard powers the NFT ecosystem, supporting platforms like OpenSea, Bored Ape Yacht Club, CryptoPunks…
- ERC-1155 - Multi-Token Standard: Created by Enjin in 2019, this standard allows a single smart contract to manage both fungible and non-fungible tokens. This makes it ideal for gaming and metaverse applications, where players need a mix of identical items (like in-game currency) and unique ones (like equipment or NFTs). ERC-1155 reduces gas costs and improves transaction efficiency via batch transfers feature, allowing sending multiple different tokens in a single transaction.
$ETH Information
$ETH Key Metrics
- Token Name: Ether
- Ticker: $ETH
- Token Type: Native Token
- Initial Total Supply: 120,698,299 ETH
- Circulating Supply: 120,698,299 ETH
Note: Ethereum does not have a fixed maximum supply; net issuance is moderated by staking rewards and token burning mechanisms.
$ETH Tokenomics
Intitial Total Supply: 120,698,299 $ETH
$ETH Allocation:
- Investors: 83.5%
- Founder & Team: 16.5%

$ETH Use Case
Ether (ETH) is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network, serving as both the fuel that powers on-chain activity and a store of value within the Web3 economy. Its versatility supports a wide range of use cases across finance, technology, and decentralized governance.
- Transaction fees (gas): Every operation on Ethereum requires gas fees paid in ETH. These fees compensate validators for processing transactions and keep the network secure against spam.
- Staking and network security: Validators lock $ETH to participate in the consensus process, earning rewards for maintaining network integrity.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Users can use $ETH to lend, borrow, trade, and earn yield through protocols such as Aave, Uniswap, Lido… turning ETH into the foundation of decentralized financial infrastructure.
- NFTs and Web3 applications: Many NFTs, gaming, marketplace platforms like OpenSea, Foundation, Zora… use ETH as their primary currency for buying, selling, and minting digital assets. It also powers millions of decentralized applications (dApps) built on Ethereum.
- A store of value: Similar to Bitcoin, many investors treat ETH as a digital asset for long-term holding and a decentralized store of value. The launch of spot Ethereum ETFs in 2024 has made ETH accessible to traditional investors, signaling growing institutional adoption and recognition of its economic value.
How to get ETH
There are two main ways to obtain Ether (ETH): buying it with money or earning it through activities. Both methods give users access to the token that powers transactions, staking, and applications across Web3.
How to buy ETH coin
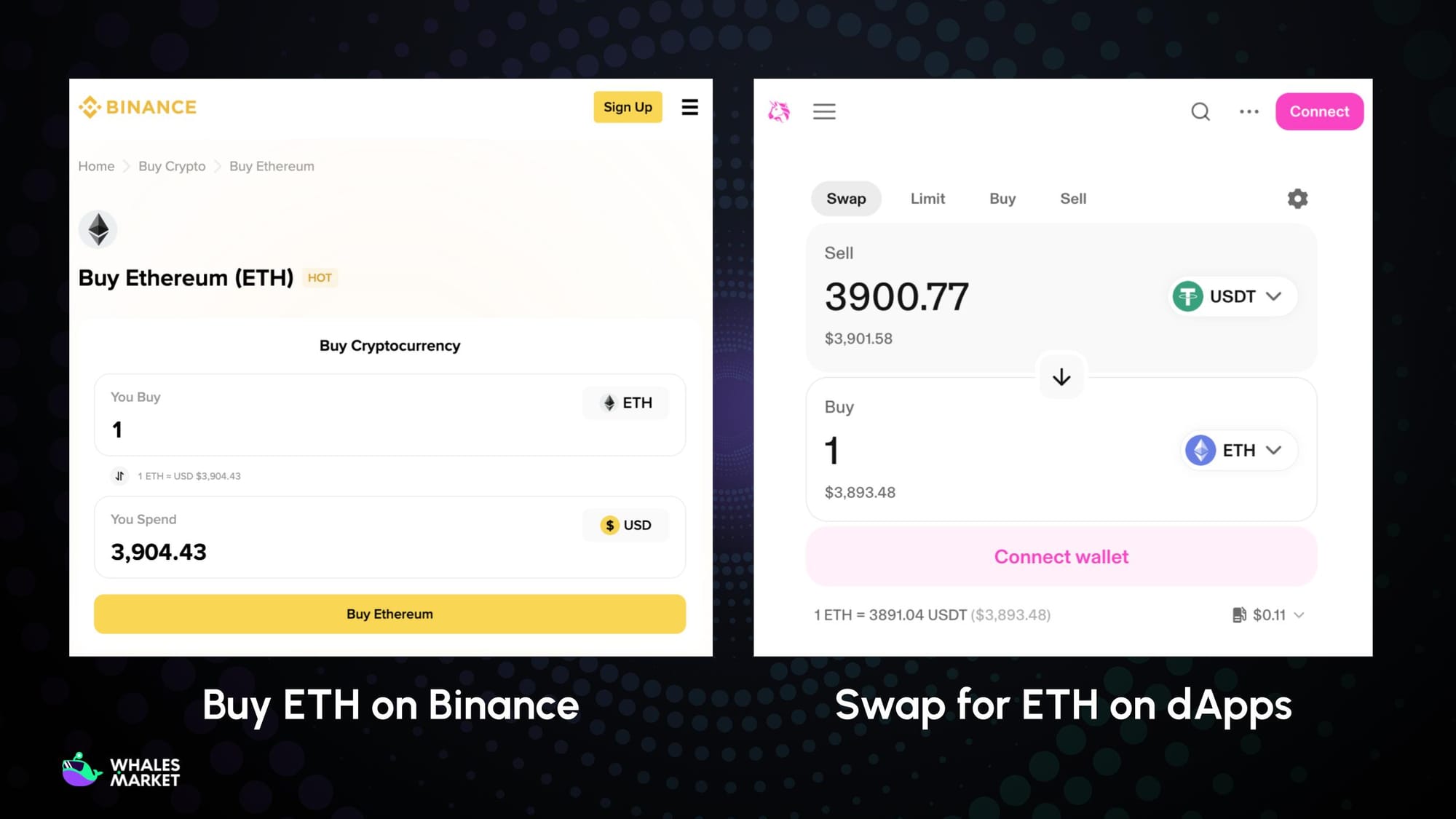
Buying $ETH on centralized exchanges (CEXs):
- This is the easiest and most popular method for beginners. Users can buy ETH through regulated crypto exchanges such as Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, or Bybit…
- They can purchase ETH with fiat currencies (USD, EUR, VND, etc.) via bank transfer, credit/debit card, or P2P trading, and then transfer it to a self-custody wallet like MetaMask for on-chain use.
Buying $ETH on decentralized exchanges (DEXs):
- ETH can also be acquired through on-chain swaps on DEXs such as Uniswap, 1inch, or PancakeSwap (BNB Chain).
- Users trade other cryptocurrencies (e.g., USDT or USDC) for ETH directly from their wallet, but must hold enough tokens to cover gas fees.
How to earn ETH coin
- Staking: By staking $ETH in the Proof-of-Stake consensus, users help secure the network and earn rewards (in $ETH). Smaller holders can join staking pools or liquid staking platforms like Lido and Rocket Pool.
- DeFi and Yield Farming: ETH holders can earn passive income by lending or providing liquidity on DeFi platforms such as Aave, Uniswap, or Ekubo, receiving interest or token rewards in return.
- Work and Bounties: Developers, freelancers, and contributors can earn ETH by working for DAOs, crypto projects, or bug bounty programs, often paid directly in Ethereum.
The team behind Ethereum
Ethereum was founded by a group of developers and visionaries who shared the goal of expanding blockchain beyond simple payments into a programmable global platform. Over time, the project has evolved under the leadership of both its original creators and a broader open-source community.

- Vitalik Buterin - Co-Founder and Chief Visionary: Proposed Ethereum in 2013 and co-founded the project. He continues to lead its research and development, focusing on scalability, Proof-of-Stake, and zero-knowledge technology.
- Gavin Wood - Co-founder and Author of the Ethereum Yellow Paper. He created the Solidity programming language and later founded Polkadot.
- Joseph Lubin - Early Financier and Organizer of Ethereum’s launch. He later founded Consensys, the company behind MetaMask and Infura.
- Other early contributors: Mihai Alisie, Anthony Di Iorio, Jeffrey Wilcke, Amir Chetrit and Charles Hoskinson (who later created Cardano) also played significant roles in Ethereum’s early formation.
Conclusion
Ethereum’s evolution shows a rare blend of resilience and reinvention. From early setbacks to groundbreaking upgrades, it has matured into the engine of decentralized innovation: a platform where finance, technology, and creativity intersect.
As Layer-2 scaling, zero-knowledge proofs, and institutional adoption accelerate, Ethereum is positioned to become the digital world’s settlement layer, shaping how the next generation builds and exchanges value online.
FAQs
Is Ethereum decentralized?
Yes. Ethereum is maintained by thousands of independent nodes worldwide. Its Proof-of-Stake consensus and open-source governance make it one of the most decentralized and transparent networks in Web3.
Why does Ethereum have value?
Ethereum’s value comes from its utility: ETH powers transactions, smart contracts, and DeFi protocols. Its deflationary burn mechanism (EIP-1559) and demand across dApps also strengthen its long-term value.
Is Ethereum a good investment? Should I buy Ethereum?
Ethereum is widely viewed as a core asset in crypto portfolios due to its strong ecosystem and institutional adoption. However, like all digital assets, ETH carries market volatility and risk, so investors should do independent research before buying.
Disclaimer: This is not financial advice!
Is Ethereum better than Bitcoin?
Not necessarily. Bitcoin is stronger as a store of value, while Ethereum excels as a platform for innovation through smart contracts and dApps. Each has its own strengths:
- Bitcoin leads in simplicity and security.
- Ethereum in flexibility and real-world utility.
How many Ethereum coins are there?
As of 2025, the total supply is about 120 million ETH, but it’s not fixed. The burn mechanism gradually reduces supply, potentially making ETH deflationary during periods of high network activity.
Who is the Ethereum founder?
Vitalik Buterin proposed Ethereum in 2013 and co-founded it with a team including Gavin Wood, Joseph Lubin, and Mihai Alisie. Vitalik remains the network’s key visionary and researcher.
How does Ethereum work?
Ethereum runs on Proof-of-Stake consensus, secured by validators who stake ETH. It uses the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) to execute smart contracts and process transactions across thousands of decentralized nodes.
What is Ethereum used for?
Ethereum powers DeFi platforms, NFTs, DAOs, gaming, and Web3 applications. ETH is used to pay gas fees, stake for network security, and interact with millions of smart contracts built on the network.

