Staking is not only a part of the blockchain economy but also the foundation of many massive narratives such as Liquid Staking and Liquid Restaking. It also plays an important role in the DeFi world by helping to capitalize the market, expand TVL, and utilize resources thoroughly without causing capital congestion.
So, what is staking? Let’s explore through the article below!
What Is Staking?
Staking is an activity where users lock a specific amount of tokens in the blockchain network in exchange for rewards. These rewards are typically based on the initial investment, including the number of tokens and the duration of the staking period.
However, staking differs from farming, where users lock tokens to receive rewards from a specific crypto project or protocol. In staking, the locked tokens not only generate profits but are also used to support transaction validation on the blockchain through the Proof of Stake mechanism.

Staking can be thought of as depositing money in a bank to receive interest after a term; it requires participants to commit a certain amount of tokens. The big difference is that stakers are not just passive investors but also directly contribute as “validators” for the blockchain network. Thanks to that, they help enhance the system’s security, transaction processing speed, and scalability, based on the Proof of Stake principle.
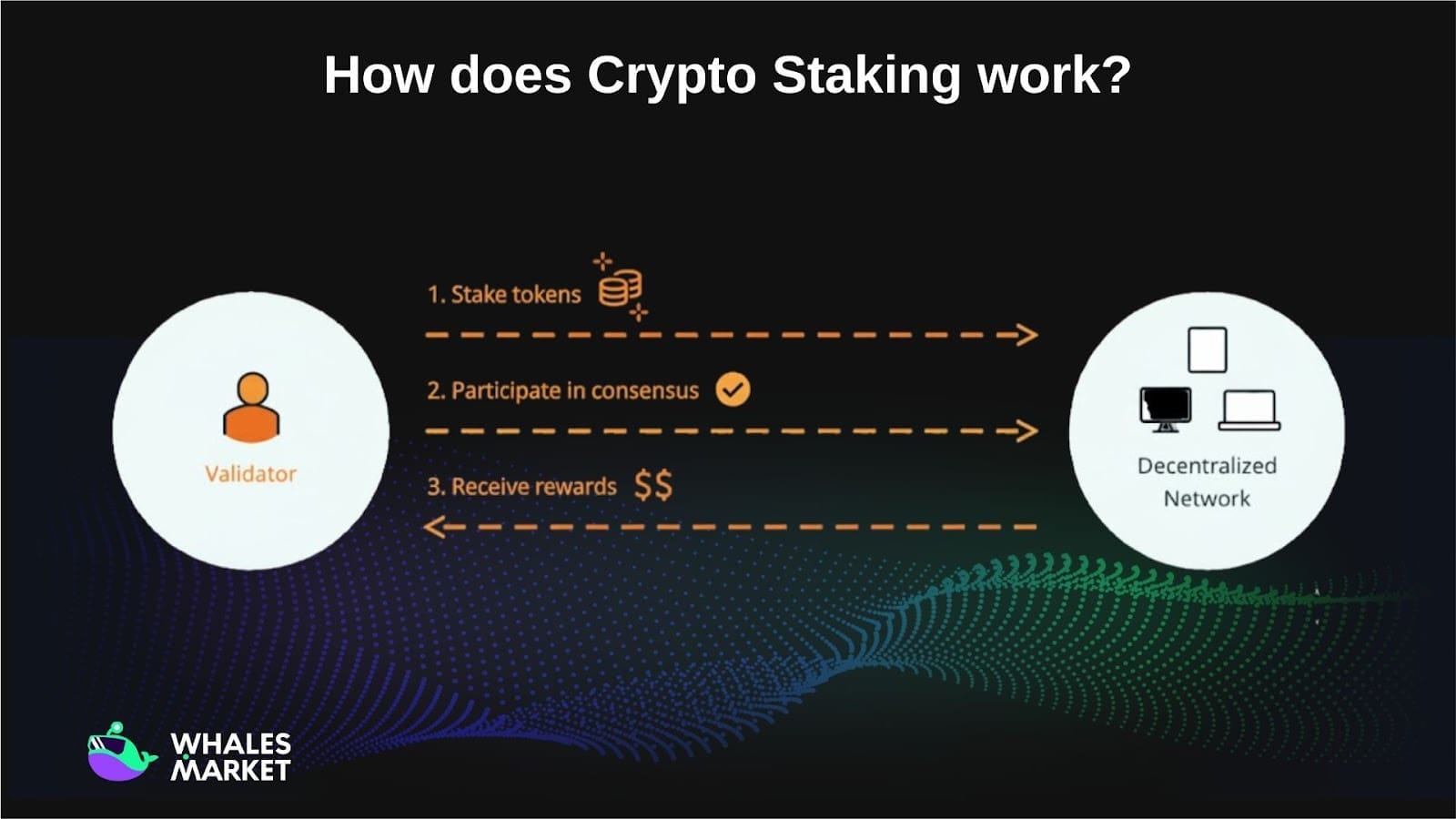
How does Crypto Staking work?
Staking operates in blockchain using the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, which is designed to be a more efficient replacement for Proof of Work (PoW).
While PoW requires miners to use hardware and consume enormous amounts of electricity to solve complex mathematical problems, PoS brings a major change by allowing users to participate in transaction validation by locking (staking) their digital assets.
This not only saves resources but also makes the network more environmentally friendly. Here’s how PoS works:
- Participants: Users who own more of the blockchain's native tokens have a higher chance of being selected as validators. These validators are responsible for checking and confirming new transactions, as well as adding them to the blockchain. In return, they receive rewards in the form of new tokens or transaction fees.
- Validator Selection Process: Users who stake more have a greater advantage, similar to a “lottery” system where the number of tickets is proportional to the committed assets. However, some PoS variants (like Delegated Proof of Stake - DPoS) allow users to delegate their stake to professional validators to increase democracy and efficiency.
- Security and Environmental Benefits: PoS minimizes network attack risks, such as 51% attacks, because attackers would need to control a large amount of tokens, which is not only costly but also reduces the value of their own tokens if successful. Moreover, this model consumes significantly less energy than PoW, contributing to reduced carbon emissions.
Different types of Staking in Crypto
Staking also exists in various styles and forms, each coming with different risks and rewards.
Solo Validator
Users lock their tokens themselves and run their own validation machines. This method gives the validator full control over the node, direct contact with the protocol and the highest share of rewards, because there is no commission fee paid to a third party.
On major PoS networks, the effective APY for solo validators is usually close to the “headline” network rate (for example, around the mid-single digits per year on large L1s, and sometimes higher on smaller chains), although returns can fluctuate over time.
However, solo validation requires a large amount of capital, stable hardware, good internet connection and the ability to maintain and upgrade the node. Any configuration error, downtime or missed upgrade can lead to slashing or loss of rewards. For this reason, solo staking is mainly used by experienced individuals or professional organizations.
Example: On Ethereum, a solo validator needs 32 ETH and must run their own validator and consensus client.
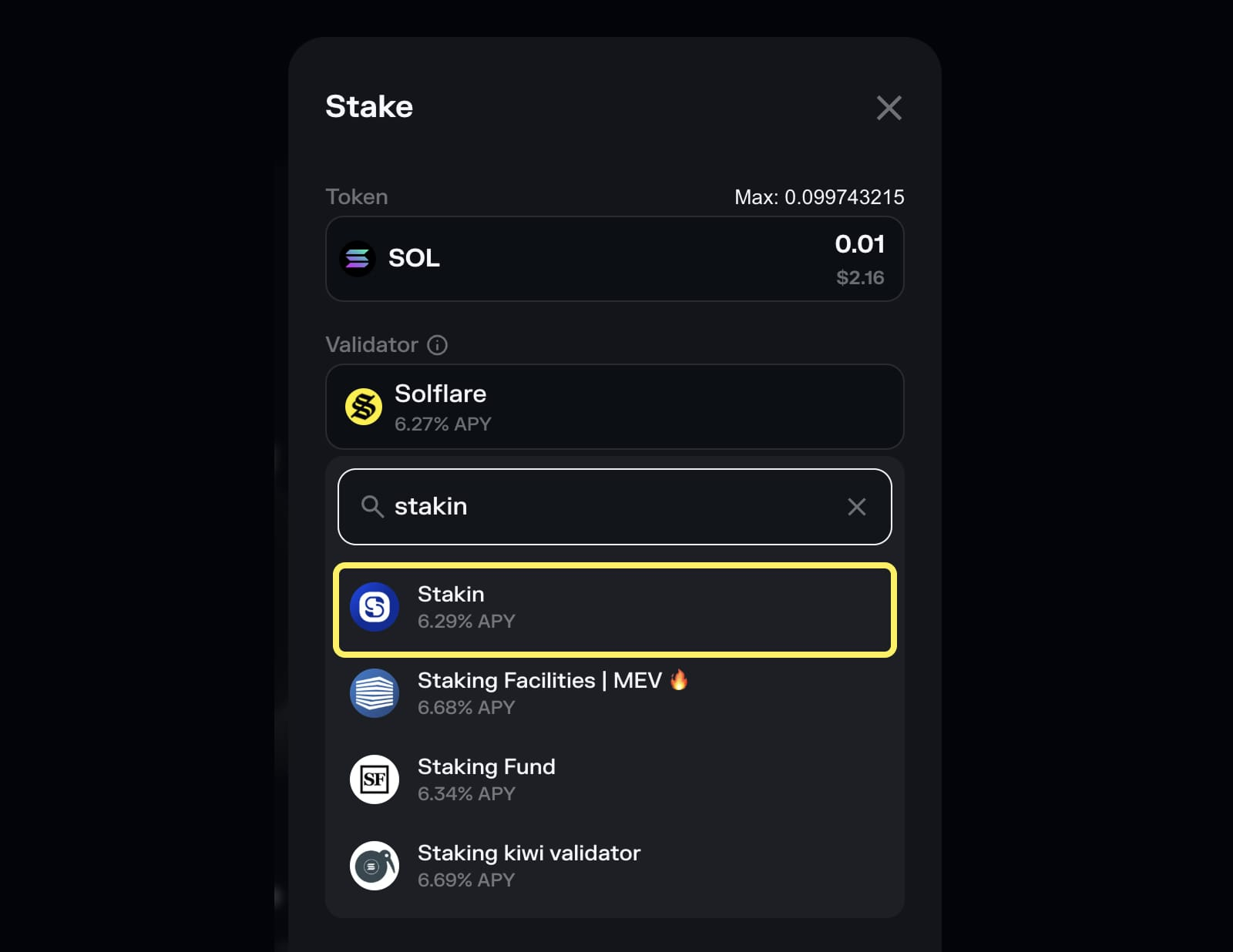
Delegation/Nomination to Validator
With delegation, users choose a trustworthy validator and delegate their tokens instead of running their own machine. The validator operates the node, and rewards from the network are shared between the validator and delegators according to a pre-agreed commission rate.
Because the validator takes a fee (often in the range of a few % to around 10-15% of the rewards, depending on the network), the effective APY for delegators is usually slightly lower than solo validation.
However, this method is much easier for most users and still offers attractive returns compared with holding tokens idle.
The main risks are dependence on the validator’s honesty and technical competence. If the validator behaves badly or fails to maintain the node, delegators can suffer slashing or missed rewards. Users should therefore spread their stake across reputable validators instead of putting everything in one place.
Example: On Solana, users can delegate SOL to validators directly from wallets such as Phantom or Solflare.
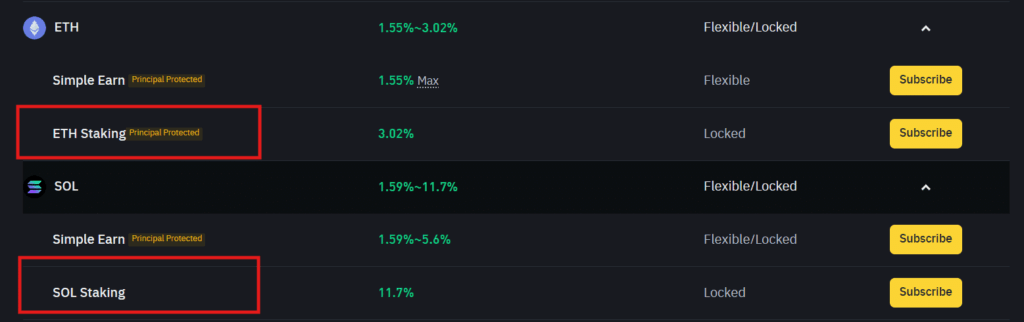
Staking via CEX
Many centralized exchanges such as Binance, Bybit or OKX offer staking or “Earn” products directly in the exchange wallet. Users simply select the asset, choose a staking product (flexible or fixed term) and confirm. There is no need to run infrastructure or interact with smart contracts, so this is one of the most convenient ways for beginners to start staking.
In terms of rewards, CEX staking usually offers rates similar to or slightly lower than on-chain delegation, because the exchange aggregates users’ funds and charges a hidden or explicit fee. Some exchanges sometimes run promotional campaigns with temporarily higher APY to attract deposits, but in general users trade a bit of yield for convenience.
The key risk here is “trust in the third party.” If the exchange is hacked, freezes withdrawals or becomes insolvent, users’ staked assets may be affected. Whether CEX staking is suitable depends on each person’s risk tolerance and preference for convenience versus self-custody.
Example: Binance ETH or SOL “Simple Earn / Staking” products in the Earn section.
Liquid Staking
In traditional staking, users lock their tokens for a period of time and cannot use them elsewhere, which limits capital efficiency. Liquid staking solves this problem by letting users stake their assets and receive a separate token in return. This token, often called a Liquid Staking Token (LST), represents the staked position and continues to accrue staking rewards.
For example:
On Ethereum, users can stake ETH through protocols such as Lido and receive stETH, an LST that tracks the value of the staked ETH plus rewards. Users can then use stETH in DeFi while still earning profits from staking the underlying ETH.
From there, the crypto space has witnessed the birth of the Liquid Staking industry worth tens of billions of USD today.
However, some risks come with this model, including:
- Depeg between the original token and LST
- Smart contract risks from Liquid Staking providers
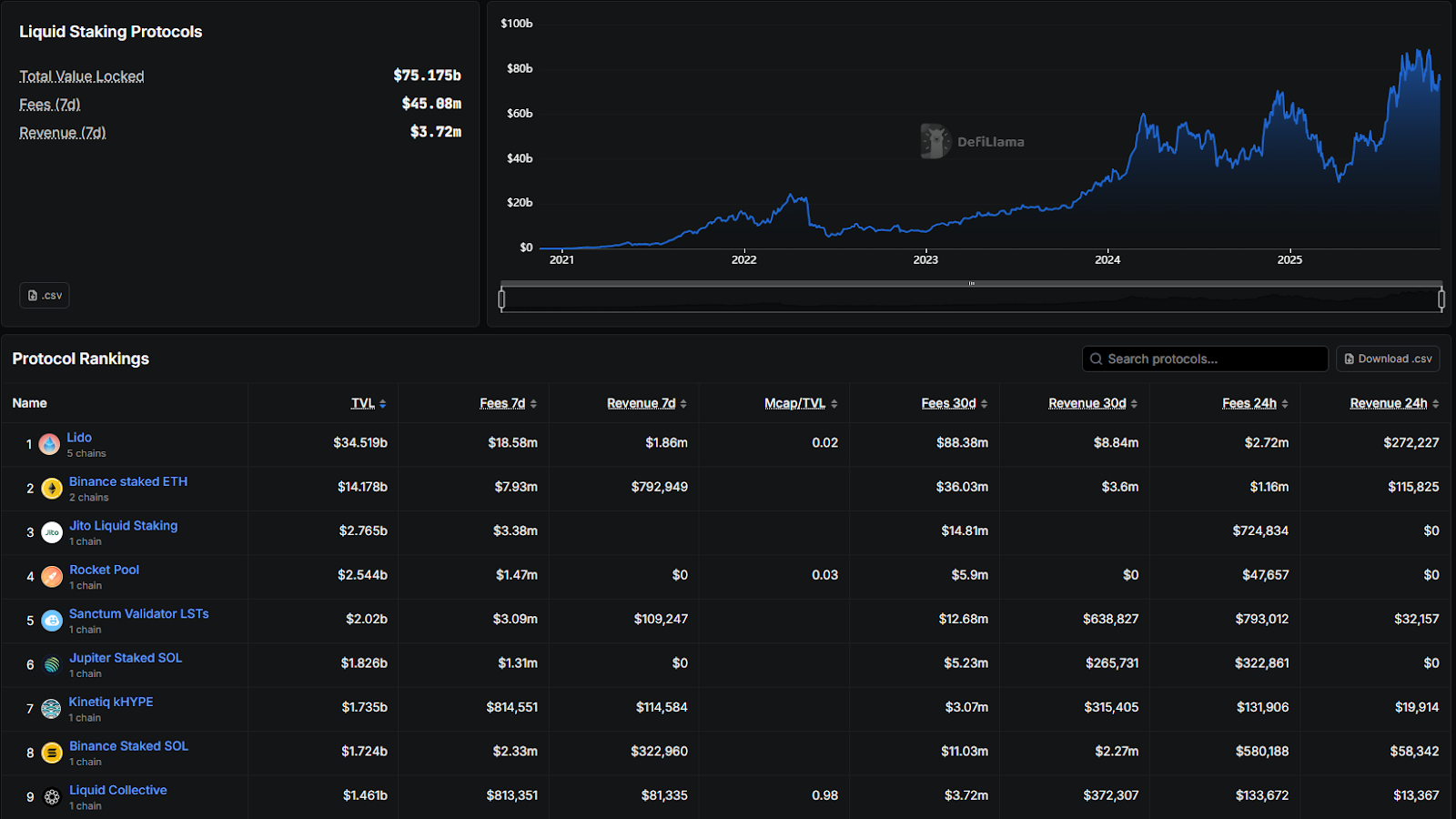
Restaking
Restaking allows the reuse of staked capital (e.g., ETH/stETH/rETH...) to secure additional services or infrastructure (oracles, data availability, sidechains/rollups...). More simply, EigenLayer reuses the value of the Ethereum network once more to protect other projects.
Restaking helps holders gain an additional layer of profits, but the risks also increase accordingly. Besides the threats from liquid staking, liquidity is now fragmented again, raising systemic and cascading risks.
For most users, there is no single “perfect” way to stake, but some methods are clearly more practical than others.
On-chain delegation/nomination
Users delegate their stake on-chain to a reputable validator.
- Users keep self-custody of their assets.
- Rewards are competitive.
- No need to run their own hardware.
- Validators handle all the technical work and node operations.
Liquid staking (for users comfortable with DeFi)
Users stake through a liquid staking protocol and receive a liquid staking token (LST).
- They earn staking rewards.
- They can also use the LST in other DeFi protocols to potentially boost returns.
But this adds extra layers of risk:
- Possible depeg events.
- Smart contract vulnerabilities.
- Governance issues in the underlying protocols.

Staking via CEX (easiest option)
Users stake directly on a centralized exchange.
- Just a few clicks to start earning yield.
- Works well for users with smaller capital or who value convenience.
However, this comes with platform risk: if the exchange is hacked or becomes insolvent, their staked assets may be at risk.
Running a solo validator (for advanced users)
Users run their own validator node.
- Generally only suitable for experienced participants.
- Requires a large stake (for example, 32 ETH on Ethereum).
- Demands time, technical skills, server maintenance, monitoring, and security.
This is closer to a semi-professional or professional activity than a simple yield strategy.
Pros and Cons of Staking
Advantages of Staking
Staking brings many benefits to crypto investors:
- No need for expensive equipment, just a compatible wallet to participate in validation, helping to save costs.
- Increases transparency and trust, as stakers directly support the network.
- Maintains asset value (no depreciation like mining machines), only affected by market fluctuations.
- Environmentally friendly due to energy savings compared to PoW.
- Reduces large-scale attack risks, enhancing system security and stability.
- Easy to participate, providing predictable profits without complex skills.
Disadvantages of Staking
Staking also comes with risks to consider:
- Locked tokens may lack liquidity during the staking period, and strong crypto price volatility can wipe out rewards or even turn a profitable position into a loss.
- Slashing events: If validators go offline or behave maliciously, a portion or even all of the staked tokens can be slashed, and validators may lose their right to validate transactions. At the market level, mass unstaking in a bear market can increase selling pressure and trigger sharp price drops.
- The time to receive rewards can be slow, and in some projects they are not paid out daily.
- Risks from validators if they mishandle funds, and from wallet or exchange hacks.
- The inflation rate of new tokens can reduce value over time.
Read more: Which is the Best Solana Wallet in 2025?
Things to Prepare Before Staking
Staking plays a key role in the health and development of the cryptocurrency market. It enhances network security by encouraging honest behavior, reduces circulating supply, and promotes long-term holding instead of speculative trading.
In the broader financial ecosystem, staking contributes to the maturation of crypto as an asset class. It offers yields often higher than traditional savings accounts, from 5% to 20% APY depending on the blockchain, attracting institutional investors and driving innovations in DeFi.
To start staking safely and effectively, prepare thoroughly:
- Research the project: Understand PoS, inflation rate (new tokens issued affects price), and interest rate (APY) to choose places with high profits but low risks.
- Wallet and tokens: Prepare a compatible wallet (e.g., native wallet or on CEX), and ensure users have the minimum required token amount.
- Locking period: Choose a suitable term, and know the waiting time for unlocking after stopping.
- Risk assessment: Prioritize safe models like liquid staking for high liquidity, use strong security (2FA), and only stake amounts users can afford to lose.
- Start small: Try with a small amount of tokens to become familiar, and diversify to reduce market risks.
FAQs
Q1. What is staking in crypto in simple terms?
Staking in crypto simply means locking your tokens on a Proof of Stake blockchain so they help secure the network. While they are locked, your tokens support validators or validate transactions, and in return you earn rewards, similar to earning interest for keeping the network running.
Q2. Why is staking important to the crypto market?
Staking plays a key role in keeping PoS blockchains secure, because stakers have economic incentives to behave honestly. It also reduces energy consumption compared with traditional mining, since it does not require intensive hardware.
For investors, staking creates a source of passive income and encourages them to hold tokens for a longer period, which can reduce speculative selling and support market stability.
Q3. Does staking have risks?
Yes, staking comes with risks. The price of the token can fall and wipe out your rewards, and you can be slashed if the validator you choose has technical issues or behaves improperly. Staked tokens are also often locked or have unbonding periods, so you may not be able to withdraw quickly when you need liquidity.
Q4. What are some popular staking coins?
Several major Proof of Stake networks support staking. Some of the most well-known examples include Ethereum (ETH), Solana (SOL), Cardano (ADA), Polkadot (DOT) and Cosmos (ATOM). These networks have large communities, established infrastructure and relatively deep liquidity, which makes them common choices for stakers.
Q5. How do staking rewards work?
Staking rewards are calculated based on how many tokens you stake and how long you keep them staked, as well as the overall performance and parameters of the network.
The protocol regularly distributes new tokens or fees to validators and delegators as compensation for securing the chain. On many large networks, the typical annual yield ranges from about 4% to 10% APY, although this rate can change over time.
Q6. How do beginners start staking?
Beginners can start by staking on centralized exchanges like Coinbase or Binance, where a few clicks are enough and the exchange handles the technical setup. Once they are more experienced, they can explore DeFi or liquid staking platforms such as Lido, which issue a liquid token so users can keep using their capital in DeFi while still earning staking rewards.
Q7. Why should you care about pre-market opportunities related to staking?
Pre-market opportunities let investors gain exposure to a token before it is officially listed on major exchanges. Many of these early-stage projects later launch staking features after TGE, so entering early can help you position yourself to start staking and earning rewards as soon as the network goes live.
Because pre-market trading happens OTC and often involves higher risk, it is important to use platforms that focus on security and escrow. Whales Market is one such platform that supports pre-market and OTC trading for tokens in a safer, more transparent way.

