In crypto, users often run into situations like “I sent coins but they have not arrived yet,” “I want to see what my wallet is holding,” or “I am not sure whether this token is real.” The tool commonly used to verify these issues is a blockchain explorer.
What is a Blockchain Explorer?
Blockchain explorer is a tool that helps users read on-chain data in an easy-to-understand way: it pulls raw data from a blockchain’s nodes, reorganizes it, and displays it through a web or API interface so users can look it up.
Simply put, a blockchain explorer can be seen as a blockchain lookup tool. Users can paste a transaction hash, wallet address, block number, or smart contract address into the search box to view the related data. Blockchain explorer is also known as block explorer.
There are many blockchain explorers in the crypto market. In general, each blockchain has one or more explorers. Common examples include Etherscan for Ethereum, BscScan for BNB Smart Chain, and Polygonscan for Polygon.
Blockchain explorers play an important role in the mission of transparency and decentralization in cryptocurrency. By making all transaction data publicly visible, they highlight a key difference between cryptocurrency and traditional money.
Common Use Cases of a Blockchain Explorer
Users can think of a blockchain explorer as a search engine for cryptocurrency and public blockchains. At a basic level, it lets users access information about transactions on specific wallet addresses and blockchains, including the amount transferred, the source and destination addresses, and the transaction status.
In general, there are 5 common ways to use a block explorer that users should know.
- Track and verify transactions: Users can use a blockchain explorer to check whether a transaction has been processed, is still pending, or has failed. This is especially useful when funds have not arrived yet or when users want to confirm transaction details.
- Check wallet balances and token holdings: By entering a wallet address, users can view the native token balance, a list of tokens held, and past transaction activity associated with that address.
- Monitor blockchain activity: Explorers allow users to see recent blocks and transactions, helping them understand overall network activity, congestion, and transaction flow on a blockchain.
- Verify smart contracts and tokens: Users can inspect smart contract addresses to confirm whether a token is legitimate, review contract interactions, and check basic contract information provided by the explorer.
- Explore blockchain data and network metrics: Many explorers provide high-level data such as token price, market cap, gas fees, and other network statistics, giving users a broader view of the blockchain’s state.
How to use a blockchain explorer?
Blockchain Transaction Tracker: How to Track Transactions
A common use case on a blockchain explorer is checking the status of a transaction. Separately, users can also paste a wallet address into the explorer search bar to see:
- Native token balance
- The list of tokens held
- Transaction history, including transfers and contract interactions
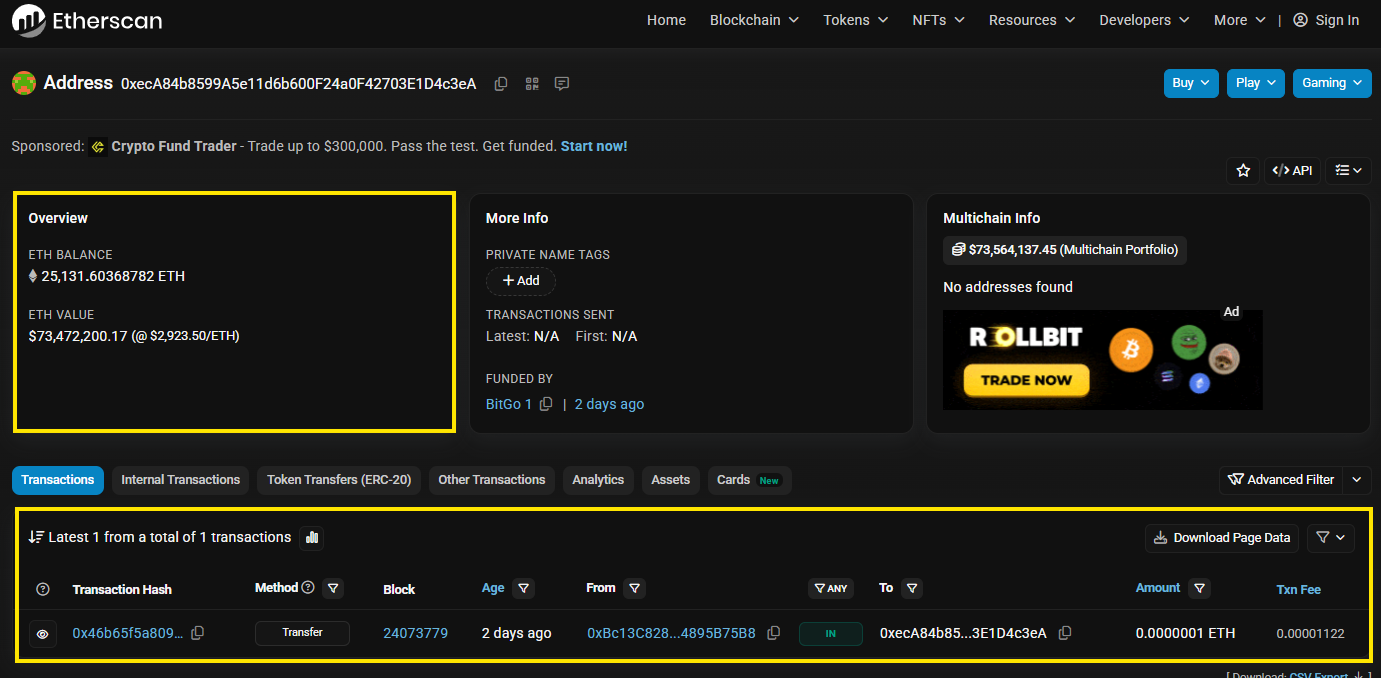
Note: An explorer shows on chain activity, not assets held on a centralized exchange. If coins are in an exchange account, the explorer will show the exchange wallet, not a personal account.
The process is similar across other chains, whether they are EVM or non-EVM blockchain. What users need to do is open the Explorer, then paste the wallet address or the txID into the search bar.
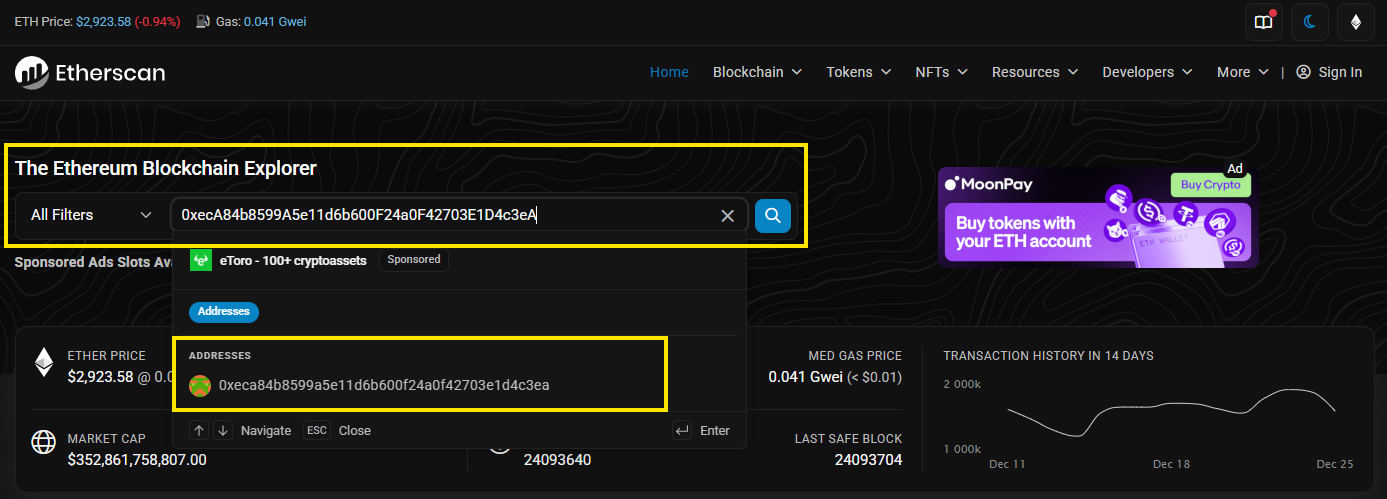
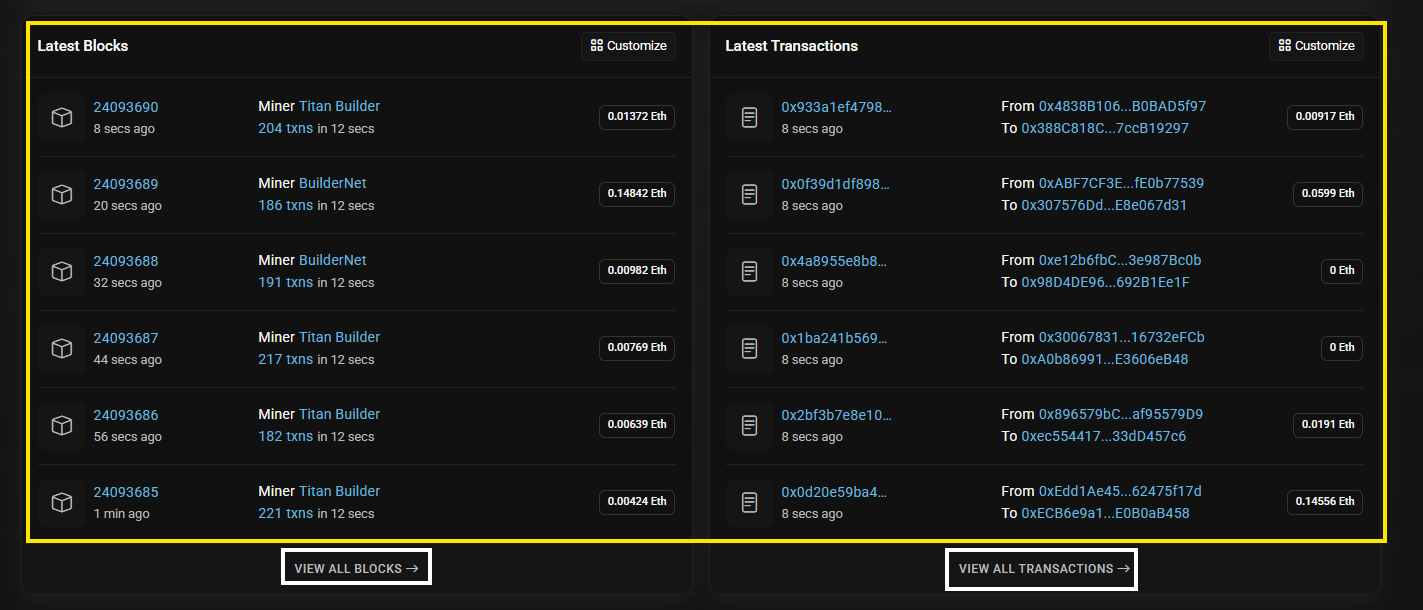
See the latest blocks and the latest transactions
On most block explorer homepages, users can also see the most recent blocks and transactions on that blockchain. Users can open a specific block to view the transactions inside it, or directly review the details of the latest transactions.
Example: On Etherscan, users can see a summary of the latest 6 blocks and the latest 6 transactions on Ethereum. If users want to see more, users can click “View all”.
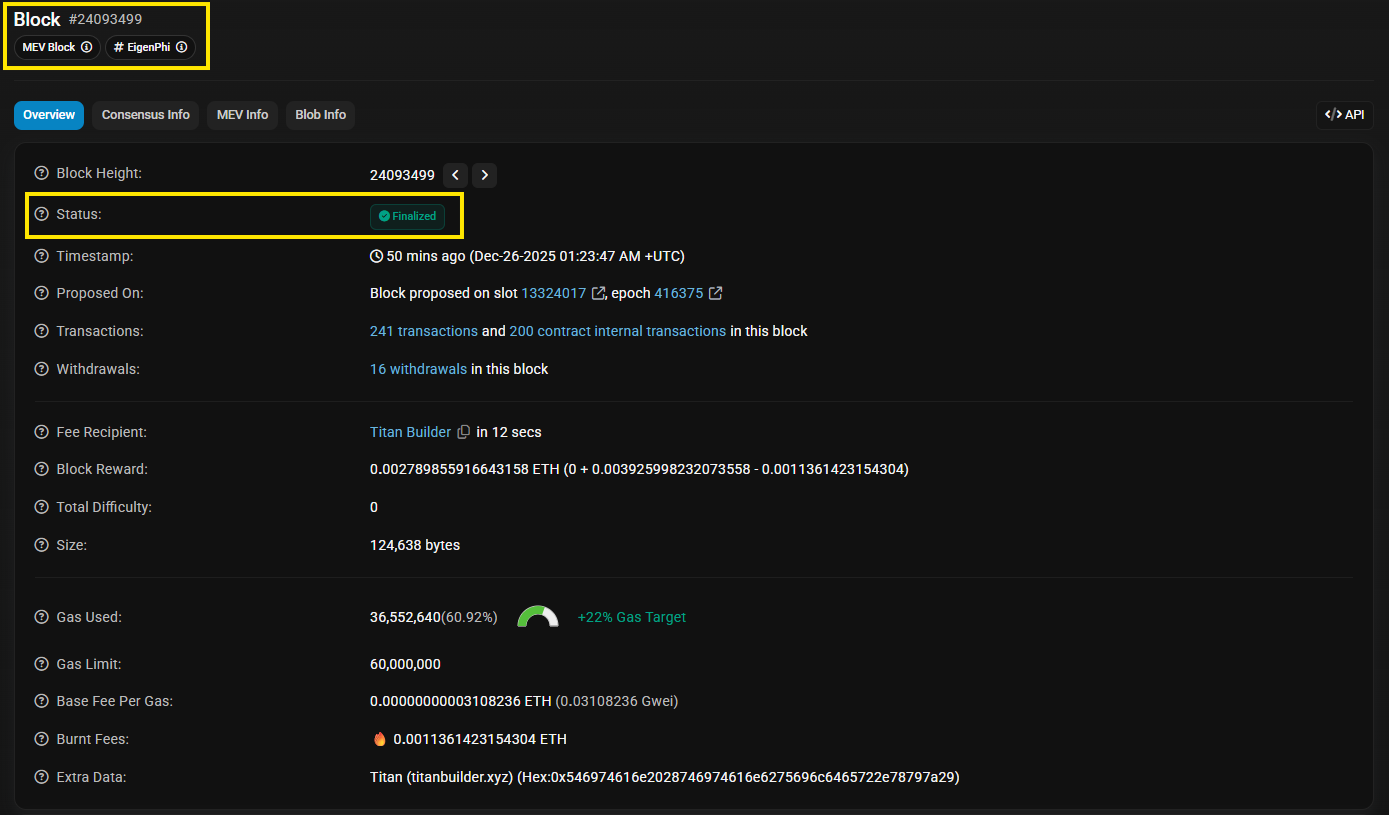
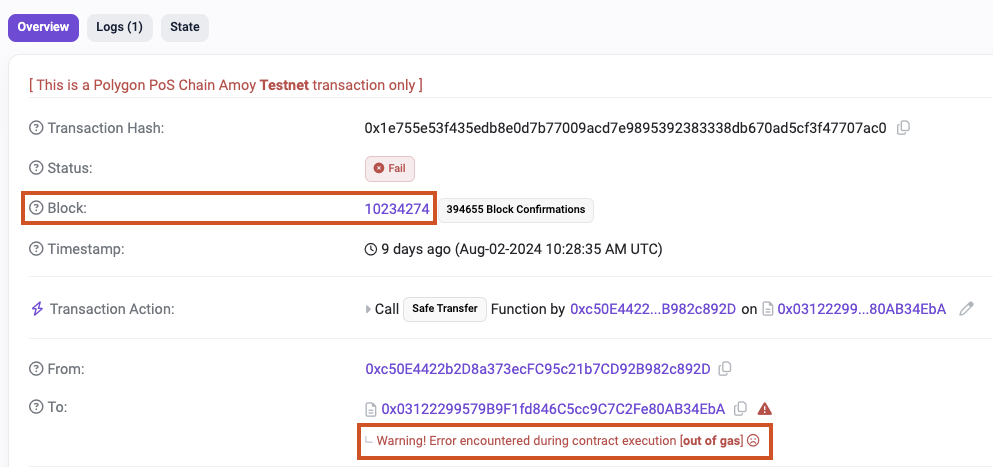
To view more details for a specific block, users can click that block. The block explorer will show a deeper overview of the block’s parameters.
Below are a few key details users should know to understand a block explorer:
- Tx hash or TxID: the unique identifier of a transaction.
- Block height: the block’s sequence number starting from the genesis block. Each new block increases the height by 1.
- From and To: the sender and receiver addresses.
- Fee and Gas: the fee paid to the network, which can be shown differently depending on the chain.
- Confirmations: the number of blocks added after the block that contains a transaction. More confirmations make the transaction harder to change if the network faces attacks.
- Pending vs Success or Fail: pending means the transaction is not yet included in a block, success means it has been included in a block and executed successfully, fail means it was included in a block but execution failed, which often happens with smart contracts.
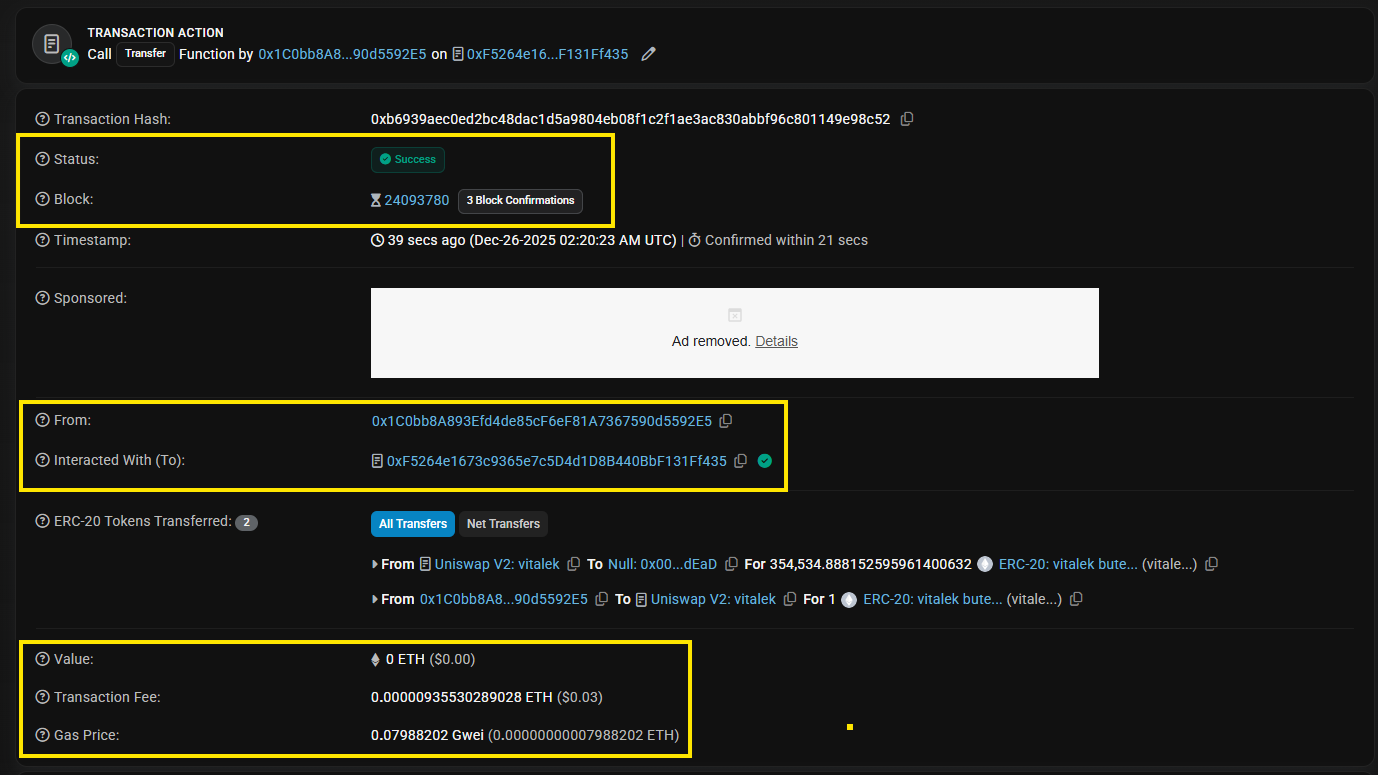
To view more details for a specific transaction, users can click that transaction. The block explorer will show a deeper overview of the transaction data. There are four key fields users should focus on:
- Status: Pending, Success, or Fail
- Block and Confirmations: whether it is included in a block and how many confirmations it has
- From and To: whether the receiving address is correct
- Value plus Fee or Gas: whether the amount and fee look reasonable
If a transaction stays pending for too long, common reasons include low fees or network congestion.
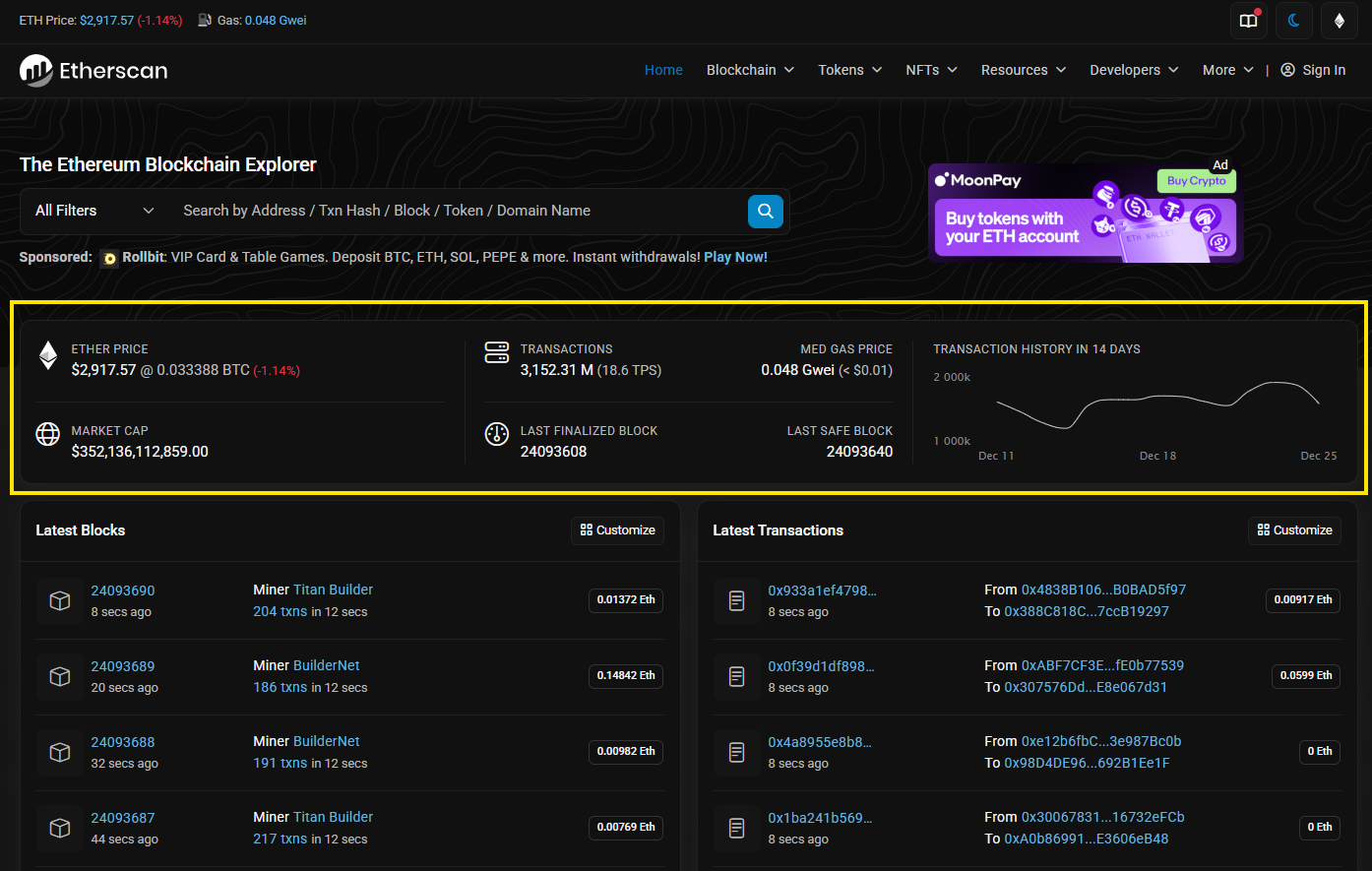
View overall blockchain information and market data
When users open the homepage of a block explorer, users can typically find an overview of that blockchain and related market data, such as:
- The native token price
- Market cap
- Blockchain stats and other blockchain level metrics
- Other related information
Some block explorers also provide deeper statistics related to market data and network data.
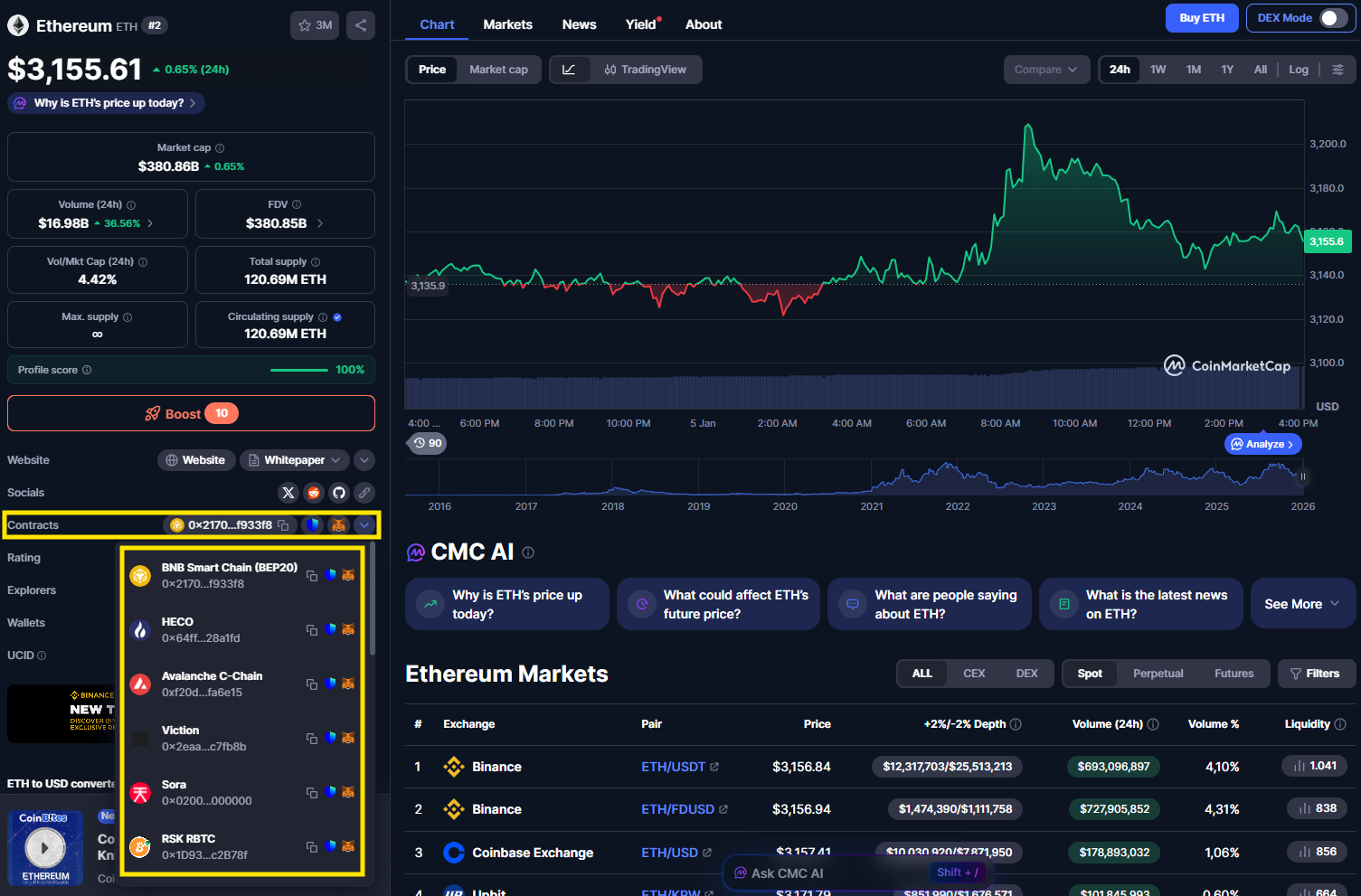
Why can users not check Token ABC on the explorer?
Explorers only support checking transactions related to tokens that are issued on the blockchain that the explorer supports. Users cannot check a token issued on Ethereum using BscScan.
If users are not sure which chain the token is on, users can visit CoinGecko or CoinMarketCap, search the token name, and then check the “Contracts” section. A token can be deployed on multiple chains.
How to Find the Explorer for a Blockchain
There are many blockchain explorers on the market, and almost every public blockchain has one or more explorers.
If users encounter a new blockchain and do not know where to find its block explorer, users can visit CoinGecko or CoinMarketCap to find the explorer information for that blockchain.
Difference Between Unconfirmed and Confirmed Transactions
When sending a crypto transaction, its status on a blockchain explorer will usually appear as either unconfirmed or confirmed. Understanding the difference helps users know whether a transaction is finalized or still in progress.
A confirmed transaction is a transaction that has been successfully included in a block. Each additional block added after that block counts as a new confirmation. More confirmations increase the security of the transaction and make it increasingly difficult to reverse or alter.
An unconfirmed transactions are transactions that have not yet been included in a block. Depending on the blockchain and the level of network congestion, a transaction may need a few minutes to receive at least one confirmation.
Which block explorer is the best?
There is no single “best” block explorer for all blockchains. The best block explorer depends on which blockchain users are using and what information they want to check.
In general, each major blockchain has one or more widely trusted explorers that are considered the standard for that network. For example, Etherscan is commonly used for Ethereum, BscScan for BNB Smart Chain, and Polygonscan for Polygon. These explorers are maintained to accurately reflect on-chain data for their respective blockchains.
A good block explorer usually has several key characteristics:
- Accurate and up to date on-chain data.
- Clear and easy to read user interface.
- Support for transactions, wallet addresses, tokens, and smart contracts.
- Reliable transaction status and confirmation information.
Some explorers also offer additional features such as analytics, gas trackers, and network statistics, which can be helpful but are not always necessary for basic use.
The most important rule is to use the correct explorer for the correct blockchain. A block explorer can only read data from the blockchain it supports, so choosing the right one ensures that the information you see is accurate and reliable.
Conclusion
Blockchain explorers are important, and anyone participating in the crypto market should learn how to use them.
In real cases such as coins not arriving, tokens not showing up, or concerns about fake tokens, an explorer is one of the fastest and most reliable ways to verify what is happening. The key point is to use the correct explorer for the correct chain, because each explorer only reads data from the blockchain it supports.
If users do not know the chain or explorer for a new project, users can check CoinGecko or CoinMarketCap to find the contract information and the corresponding explorer link.
FAQs
Q1. How to check a crypto transaction on a blockchain explorer?
To check a crypto transaction, users simply paste the transaction hash (TxID) into the search bar of a blockchain explorer. The explorer will display key details such as transaction status, confirmation count, sender and receiver addresses, transaction value, and fees.
Q2. What is a transaction hash (TxID) and where to find it?
A transaction hash, or TxID, is a unique identifier assigned to every blockchain transaction. It allows users to track and verify transactions on-chain and can usually be found in wallet apps, exchange withdrawal histories, or transaction detail pages.
Q3. Why is a transaction pending on Etherscan or BscScan?
A transaction may remain pending when the network is congested or when the gas fee set is too low compared to current demand. In such cases, miners or validators prioritize transactions with higher fees, causing delays for others.
Q4. How many confirmations are needed for a transaction to be confirmed?
The number of confirmations required depends on the blockchain network and the platform’s security policy. Users can always check the current confirmation count directly on the transaction page of a blockchain explorer.
Q5. How to check wallet balance and token holdings on a blockchain explorer?
Users can check their wallet balance by pasting the wallet address into a blockchain explorer. This allows them to view native token balances, token holdings, and full transaction history without connecting a wallet.

